Can You Use a Leaf Blower with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction? 10 Expert Tips
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) occurs when the tubes connecting the middle ear to the throat, responsible for balancing ear pressure and draining fluids, become blocked or fail to function properly. This condition can make activities involving changes in air pressure, such as using a can you use a leaf blower with eustachian tube dysfunction, particularly uncomfortable. People with ETD may experience discomfort or pain during such activities due to the pressure fluctuations.
In this article, we explore whether it’s advisable to use a leaf blower if you have ETD. We will discuss the potential risks, offer tips for safer yard work, and suggest strategies to minimize discomfort. If you’re managing ETD, understanding these precautions can help you perform outdoor tasks with greater ease and comfort.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Understanding the Condition
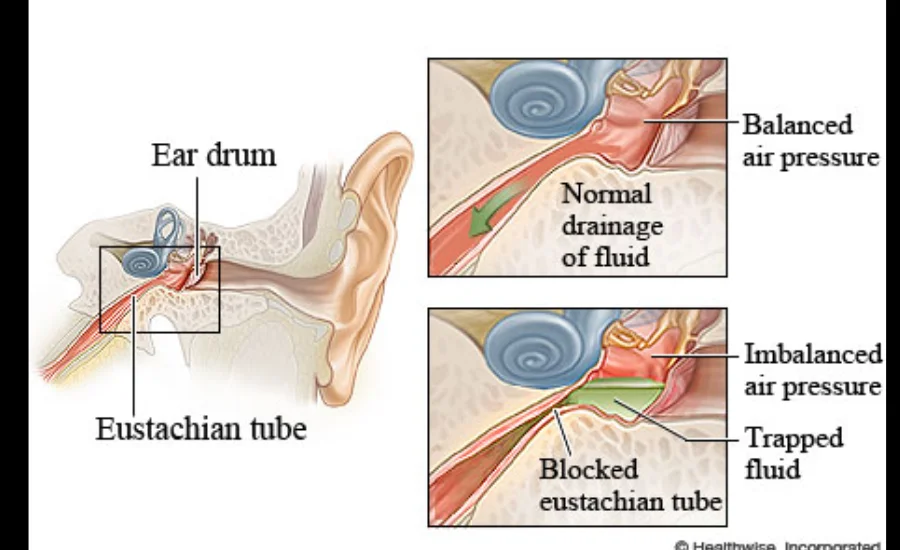
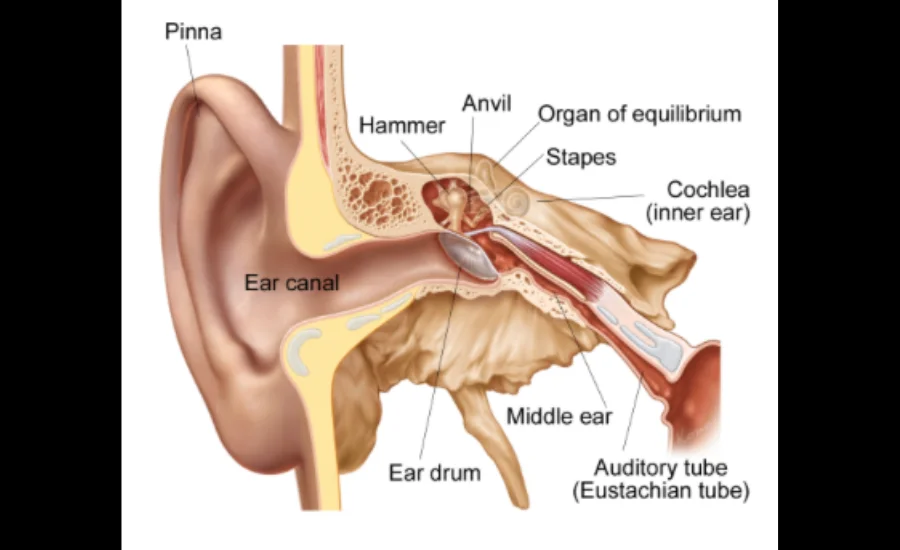
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) is a condition where the Eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the back of the throat, are not functioning as they should. These tubes play an important role in maintaining ear pressure balance, draining fluids, and protecting the middle ear from infections. When ETD occurs, the tubes become blocked, inflamed, or fail to open properly, leading to discomfort and a variety of symptoms such as a feeling of fullness in the ear, ear pain, and difficulty hearing. ETD can result from a number of factors including infections, allergies, sinus problems, or changes in altitude or air pressure.
People with ETD often face challenges when it comes to managing their daily activities, particularly those involving loud noises, pressure changes, or vibrations. This condition can make seemingly normal tasks like flying, diving, or even using household tools feel uncomfortable or painful. For those with ETD, understanding how external factors like noise and air pressure affect ear health is critical to minimizing discomfort and managing symptoms effectively.
How ETD Affects Ear Pressure and Fluid Drainage
The Eustachian tubes are responsible for equalizing air pressure between the middle ear and the outside environment. This equalization process is crucial for hearing and preventing discomfort. When these tubes malfunction, the middle ear can become overly pressurized, leading to a feeling of fullness, discomfort, or even pain. Additionally, the Eustachian tubes help drain fluids from the middle ear to the back of the throat, preventing fluid buildup that could lead to infections. When the tubes become blocked, this drainage is hindered, which can also contribute to the symptoms associated with ETD.
Several factors can contribute to ETD, including upper respiratory infections, sinusitis, allergies, or even sudden changes in air pressure. For example, activities like flying, diving, or driving through mountainous regions can trigger pressure changes that the Eustachian tubes cannot equalize properly, leading to discomfort. In individuals with ETD, these symptoms can become more pronounced, causing greater difficulty in managing the condition.
The Impact of can you use a leaf blower with eustachian tube dysfunction
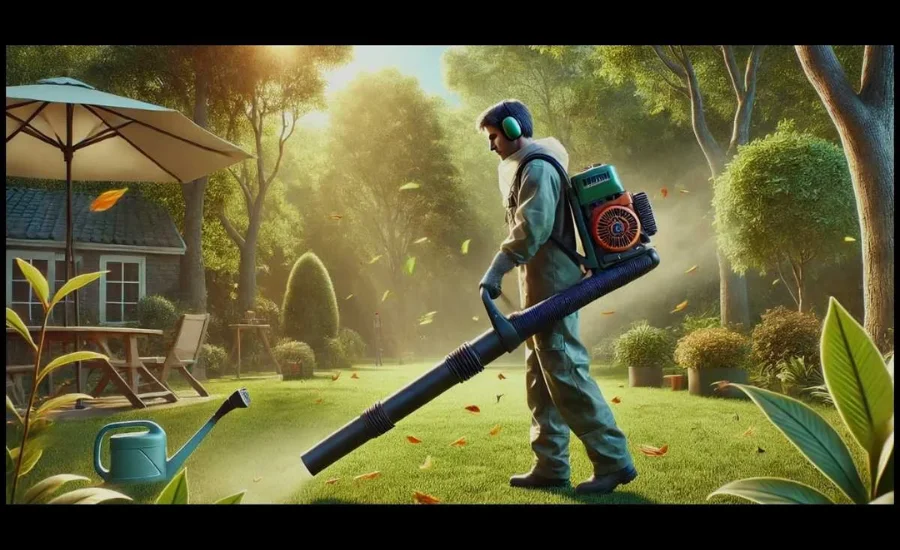

When using a leaf blower, individuals with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) may experience significant discomfort due to the intense noise and pressure changes generated by the device. Leaf blowers are powerful tools designed to efficiently clear leaves and debris by producing high-speed airflow. While this airflow is effective at moving debris, it also creates substantial noise and vibrations, both of which can be problematic for individuals with ETD.
The primary concern for people with ETD when using a leaf blower is the loud noise generated by these machines. Leaf blowers typically produce sound levels ranging from 90 to 110 decibels, which is significantly louder than everyday sounds like conversations (which are around 60 decibels). Prolonged exposure to such high noise levels can be harmful to the ears, especially for those with ETD, as their Eustachian tubes are already compromised and struggle to balance ear pressure effectively. The loud noise from the blower can intensify symptoms like ear fullness, discomfort, and even lead to temporary hearing loss if used without proper protection.
In addition to the noise, the high-speed airflow created by the leaf blower can cause rapid pressure changes around the ear. This increase in air pressure can put additional strain on the already malfunctioning Eustachian tubes, exacerbating symptoms such as ear pain, pressure, and discomfort. For someone with ETD, this added pressure can be particularly challenging, as the Eustachian tubes are responsible for equalizing the pressure between the middle ear and the outside environment. If the tubes are unable to open and close properly, the changes in pressure caused by the blower can worsen the condition, potentially leading to a sensation of blockage or fullness.
Vibrations from the machine can further impact the inner ear, which plays a crucial role in maintaining balance. For individuals with ETD who already experience balance issues or dizziness, the vibrations from the blower can intensify these symptoms, making it difficult to safely operate the machine. These combined factors—loud noise, pressure changes, and vibrations—make using a leaf blower particularly troublesome for those with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction.
Risks of Using a Leaf Blower with ETD
For individuals with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction, using a leaf blower presents several risks that could exacerbate symptoms. The loud noise generated by leaf blowers is a primary concern, as prolonged exposure to high decibel levels can lead to noise-induced hearing damage. These high noise levels can be particularly problematic for those with ETD, as the pressure and vibrations from the blower may worsen symptoms like ear fullness, pain, and hearing loss.
Leaf blowers typically generate noise levels ranging between 90 and 110 decibels, far exceeding the sound levels of normal conversation (around 60 decibels). Prolonged exposure to sounds above 85 decibels can damage hearing over time, especially for those with pre-existing ear conditions. This damage can lead to temporary or permanent hearing loss, as well as an increased risk of tinnitus, a condition characterized by ringing in the ears.
Additionally, the air pressure produced by a leaf blower can create added strain on the already compromised Eustachian tubes. The force of the air could exacerbate the discomfort caused by ETD, leading to increased pressure and a sense of fullness in the ear. In some cases, this may even lead to ear barotrauma, a condition where the ear is injured due to sudden or extreme changes in pressure.
Vibration is another factor to consider when using a leaf blower. The vibrations produced by the machine can affect the balance organs within the inner ear, which are responsible for maintaining equilibrium. Individuals with ETD who are already prone to dizziness or balance problems may find these vibrations intensify their symptoms, making it difficult to use the leaf blower safely.
How to Safely Use a Leaf Blower with ETD
For individuals determined to use a leaf blower despite the risks associated with ETD, there are several precautions that can help minimize the potential for discomfort or injury.
Choosing the Right Leaf Blower
The first step in using a leaf blower with ETD is to select the appropriate equipment. Opting for a blower with adjustable speed settings can help reduce both noise levels and air pressure, making it less likely to exacerbate ETD symptoms. Lowering the speed can significantly reduce the strain on the ears and help maintain a more comfortable experience. Additionally, quieter models are available, which can provide an ear-friendly alternative to traditional, louder blowers.
Wearing Ear Protection
One of the most effective ways to protect your ears from the loud noise produced by a leaf blower is to wear high-quality ear protection. Noise-canceling headphones or earplugs can help reduce the impact of the blower’s sound, minimizing the risk of aggravating ETD symptoms. Investing in good ear protection is crucial, especially for individuals who need to use a leaf blower frequently or for extended periods.
Taking Breaks and Limiting Use
Even with the right equipment and ear protection, it is important to limit exposure to the loud noise and air pressure generated by the leaf blower. Taking frequent breaks during yard work can give the ears a chance to recover and reduce the risk of discomfort. Prolonged use of a leaf blower should be avoided, especially if symptoms of ETD worsen during or after use.
Exploring Alternative Yard Maintenance Methods
For individuals with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) who find that using a leaf blower aggravates their symptoms, exploring alternative yard maintenance methods is a wise decision. Leaf blowers, while efficient, can trigger discomfort due to their loud noise, air pressure, and vibrations. Fortunately, several alternatives are available that may reduce the risk of exacerbating ETD symptoms while still allowing for effective yard work.
One of the most straightforward alternatives is raking leaves by hand. While this method is more physically demanding than using a leaf blower, it eliminates the noise and air pressure associated with blowers. Raking provides a quieter, more controlled approach to yard work, reducing the risk of ear discomfort and ear pressure imbalances. The physical exertion involved can be taxing, but it offers a gentler option for individuals with ETD, as it avoids the environmental triggers that exacerbate their condition. For those concerned about the physical strain, regular breaks and alternating tasks with other methods can make the process more manageable.
Another effective alternative is using a broom or sweeping leaves manually. This method also eliminates the loud noise generated by leaf blowers and is ideal for smaller yards or areas with less debris. Like raking, using a broom avoids air pressure changes and vibrations, providing a safer option for those with ETD. The quiet operation of a broom makes it an excellent choice for people sensitive to sound, particularly if their ETD symptoms are worsened by loud noises.
Additionally, electric leaf vacuums are a viable alternative. These machines tend to produce less noise and vibration compared to traditional gas-powered blowers. While they still generate some noise, they are generally quieter and cause less disruption to ear health, making them a better option for those managing ETD. Electric leaf vacuums combine the efficiency of a blower with reduced noise levels, offering a more ear-friendly solution for yard maintenance.
By considering these alternatives, individuals with ETD can continue to care for their yards while minimizing the risks associated with leaf blowers.
Regular Management of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Effectively managing Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) is crucial for minimizing discomfort and preventing the condition from worsening. Regular treatment, guided by a healthcare provider, plays a significant role in controlling ETD and alleviating symptoms. The right approach can help restore balance to the Eustachian tubes, improving ear pressure regulation and reducing discomfort.
For mild symptoms, simple techniques can be quite helpful. Swallowing, yawning, or chewing gum are natural methods that encourage the Eustachian tubes to open and close, allowing them to equalize ear pressure. These actions are often effective in relieving the feeling of fullness or slight discomfort caused by pressure imbalances. While these methods may not fully resolve the issue in more severe cases, they can provide temporary relief and help individuals manage mild symptoms more comfortably throughout the day.
For more severe cases of ETD, additional treatments may be necessary. Nasal decongestants or allergy medications can be used to reduce inflammation or congestion that may be contributing to Eustachian tube dysfunction. Decongestants help open up the nasal passages and reduce swelling in the Eustachian tubes, allowing for better pressure equalization. For individuals whose ETD is triggered by allergies, antihistamines or corticosteroids may be recommended to control symptoms and reduce the likelihood of flare-ups.
In addition to treatments, avoiding known triggers is essential in managing ETD effectively. Loud noises and sudden changes in air pressure can exacerbate symptoms, so individuals with ETD should take extra care to avoid these situations when possible. This may include using ear protection in noisy environments, avoiding activities that cause rapid pressure changes (like flying or diving), and taking steps to protect the ears during activities that involve loud sounds or intense vibrations.
By managing these factors, individuals with ETD can improve their ear health, reduce discomfort, and prevent further complications associated with the condition.
Final Words
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) occurs when the tubes connecting the middle ear to the throat become blocked or fail to function properly, leading to symptoms like ear fullness, pain, and difficulty hearing. This condition can make activities involving loud noise or air pressure changes, such as using a leaf blower, particularly uncomfortable. Leaf blowers produce intense noise, vibrations, and high-speed airflow, which can exacerbate ETD symptoms by straining the compromised Eustachian tubes.
To minimize risks, consider alternatives like raking or using a broom, which avoid the noise and pressure associated with blowers. Electric leaf vacuums are also quieter, offering a safer option for those with ETD. If using a leaf blower is unavoidable, choose quieter models, wear ear protection, and take frequent breaks to limit exposure.
Managing ETD involves regular treatment, such as using decongestants or allergy medications, and avoiding triggers like loud noises and pressure changes. Simple techniques like yawning or chewing gum can also help equalize ear pressure and alleviate discomfort.
FAQs
1. What is Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD)?
ETD occurs when the Eustachian tubes connecting the middle ear to the throat become blocked or fail to function properly. This leads to symptoms like ear fullness, pain, and difficulty hearing.
2. How does a leaf blower affect ETD?
The intense noise, vibrations, and pressure changes generated by leaf blowers can exacerbate ETD symptoms, causing discomfort, ear pain, or a sensation of fullness.
3. What are the risks of using a leaf blower with ETD?
Risks include increased ear pressure, worsening of symptoms like pain and fullness, potential temporary hearing loss, and exposure to damaging noise levels.
4. What precautions can I take if I must use a leaf blower?
Use quieter models, wear ear protection, reduce the speed setting, and take frequent breaks to limit exposure to noise and vibrations.
5. Are there alternatives to using a leaf blower?
Yes, alternatives include raking, sweeping with a broom, or using electric leaf vacuums, which are quieter and produce less vibration.
6. How can I manage ETD symptoms during yard work?
Take regular breaks, wear ear protection, and avoid activities that expose you to loud noises or sudden air pressure changes.
7. Can ETD be treated?
Yes, ETD can be managed with treatments such as nasal decongestants, allergy medications, or simple techniques like yawning and swallowing to equalize ear pressure.
8. How loud are leaf blowers, and why are they problematic?
Leaf blowers typically produce noise levels between 90–110 decibels, which can harm hearing and exacerbate ETD symptoms.
9. What triggers should individuals with ETD avoid?
Avoid loud noises, sudden air pressure changes (like flying or diving), and environments with intense vibrations to prevent symptom flare-ups.
10. When should I consult a doctor about ETD?
If symptoms persist, worsen, or significantly impact daily activities, seek advice from a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment.
Find expert advice and helpful tips on managing Eustachian Tube Dysfunction only at Insight Graze!






